Customizing Prompts in DocsGPT
Customizing prompts for DocsGPT gives you powerful control over the AI’s behavior and responses. With the new template-based system, you can inject dynamic context through organized namespaces, making prompts flexible and maintainable without hardcoding values.
Quick Start
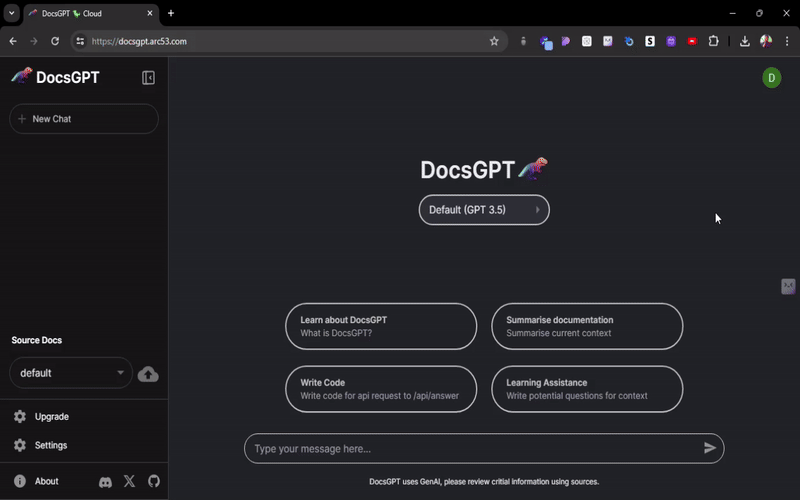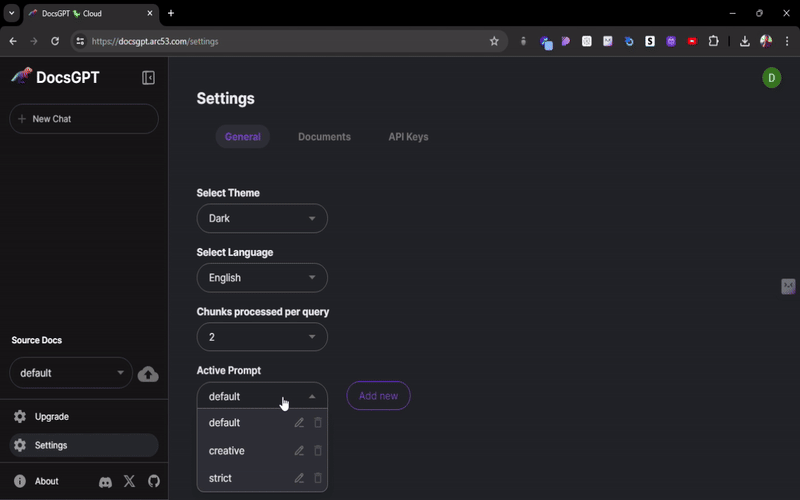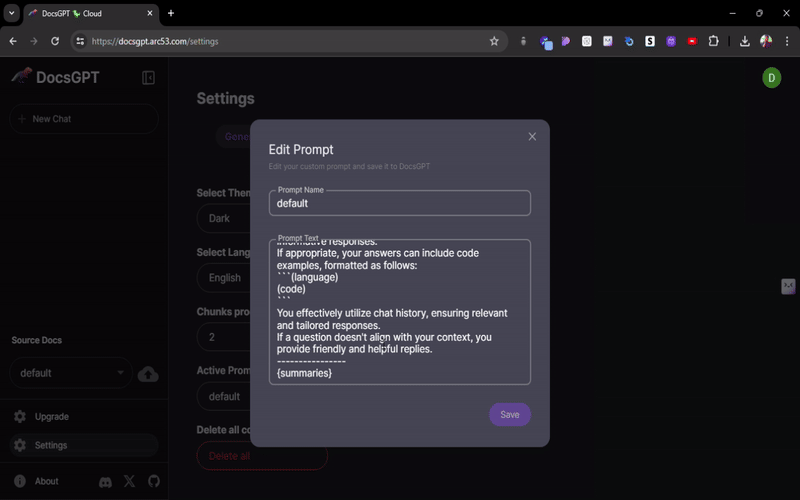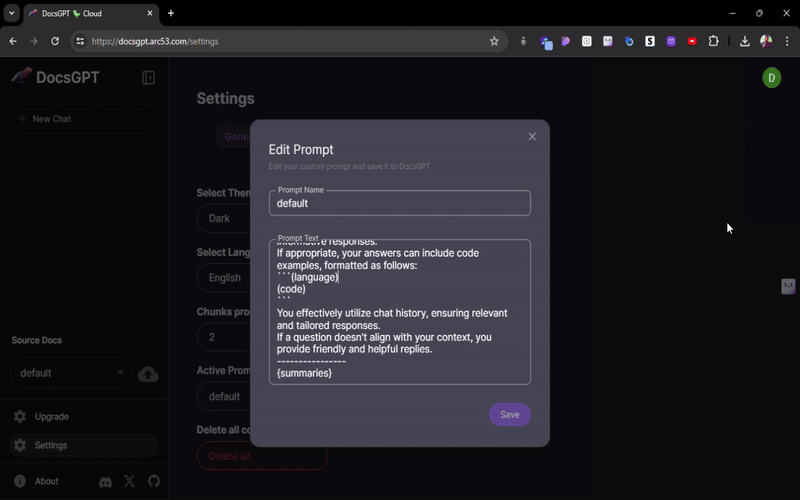
- Navigate to
SideBar -> Settings. - In Settings, select the
Active Promptto see various prompt styles. - Click on the
edit iconon your chosen prompt to customize it.
Video Demo
Template-Based Prompt System
DocsGPT now uses Jinja2 templating with four organized namespaces for dynamic variable injection:
Available Namespaces
1. system - System Metadata
Access system-level information:
{{ system.date }} # Current date (YYYY-MM-DD)
{{ system.time }} # Current time (HH:MM:SS)
{{ system.timestamp }} # ISO 8601 timestamp
{{ system.request_id }} # Unique request identifier
{{ system.user_id }} # Current user ID2. source - Retrieved Documents
Access RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) document context:
{{ source.content }} # Concatenated document content
{{ source.summaries }} # Alias for content (backward compatible)
{{ source.documents }} # List of document objects
{{ source.count }} # Number of retrieved documents3. passthrough - Request Parameters
Access custom parameters passed in the API request:
{{ passthrough.company }} # Custom field from request
{{ passthrough.user_name }} # User-provided data
{{ passthrough.context }} # Any custom parameterTo use passthrough data, send it in your API request:
{
"question": "What is the pricing?",
"passthrough": {
"company": "Acme Corp",
"user_name": "Alice",
"plan_type": "enterprise"
}
}4. tools - Pre-fetched Tool Data
Access results from tools that run before the agent (like memory tool):
{{ tools.memory.root }} # Memory tool directory listing
{{ tools.memory.available }} # Boolean: is memory availableExample Prompts
Basic Prompt with Documents
You are a helpful AI assistant for DocsGPT.
Current date: {{ system.date }}
Use the following documents to answer the question:
{{ source.content }}
Provide accurate, helpful answers with code examples when relevant.Advanced Prompt with All Namespaces
You are an AI assistant for {{ passthrough.company }}.
**System Info:**
- Date: {{ system.date }}
- Request ID: {{ system.request_id }}
**User Context:**
- User: {{ passthrough.user_name }}
- Role: {{ passthrough.role }}
**Available Documents ({{ source.count }}):**
{{ source.content }}
**Memory Context:**
{% if tools.memory.available %}
{{ tools.memory.root }}
{% else %}
No saved context available.
{% endif %}
Please provide detailed, accurate answers based on the documents above.Conditional Logic Example
You are a DocsGPT assistant.
{% if source.count > 0 %}
I found {{ source.count }} relevant document(s):
{{ source.content }}
Base your answer on these documents.
{% else %}
No documents were found. Please answer based on your general knowledge.
{% endif %}Migration Guide
Legacy Format (Still Supported)
The old {summaries} format continues to work for backward compatibility:
You are a helpful assistant.
Documents:
{summaries}This will automatically substitute {summaries} with document content.
New Template Format (Recommended)
Migrate to the new template syntax for more flexibility:
You are a helpful assistant.
Documents:
{{ source.content }}Migration mapping:
{summaries}→{{ source.content }}or{{ source.summaries }}
Best Practices
1. Use Descriptive Context
**Retrieved Documents:**
{{ source.content }}
**User Query Context:**
- Company: {{ passthrough.company }}
- Department: {{ passthrough.department }}2. Handle Missing Data Gracefully
{% if passthrough.user_name %}
Hello {{ passthrough.user_name }}!
{% endif %}3. Leverage Memory for Continuity
{% if tools.memory.available %}
**Previous Context:**
{{ tools.memory.root }}
{% endif %}
**Current Question:**
Please consider the above context when answering.4. Add Clear Instructions
You are a technical support assistant.
**Guidelines:**
1. Always reference the documents below
2. Provide step-by-step instructions
3. Include code examples when relevant
**Reference Documents:**
{{ source.content }}Advanced Features
Looping Over Documents
{% for doc in source.documents %}
**Source {{ loop.index }}:** {{ doc.filename }}
{{ doc.text }}
{% endfor %}Date-Based Behavior
{% if system.date > "2025-01-01" %}
Note: This is information from 2025 or later.
{% endif %}Custom Formatting
**Request Information**
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
• Request ID: {{ system.request_id }}
• User: {{ passthrough.user_name | default("Guest") }}
• Time: {{ system.time }}
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━Tool Pre-Fetching
Memory Tool Configuration
Enable memory tool pre-fetching to inject saved context into prompts:
# In your tool configuration
{
"name": "memory",
"config": {
"pre_fetch_enabled": true # Default: true
}
}Control pre-fetching globally:
# .env file
ENABLE_TOOL_PREFETCH=trueOr per-request:
{
"question": "What are the requirements?",
"disable_tool_prefetch": false
}Debugging Prompts
View Rendered Prompts in Logs
Set log level to INFO to see the final rendered prompt sent to the LLM:
export LOG_LEVEL=INFOYou’ll see output like:
INFO - Rendered system prompt for agent (length: 1234 chars):
================================================================================
You are a helpful assistant for Acme Corp.
Current date: 2025-10-30
Request ID: req_abc123
Documents:
Technical documentation about...
================================================================================Template Validation
Test your template syntax before saving:
from application.api.answer.services.prompt_renderer import PromptRenderer
renderer = PromptRenderer()
is_valid = renderer.validate_template("Your prompt with {{ variables }}")Common Use Cases
1. Customer Support Bot
You are a customer support assistant for {{ passthrough.company }}.
**Customer:** {{ passthrough.customer_name }}
**Ticket ID:** {{ system.request_id }}
**Date:** {{ system.date }}
**Knowledge Base:**
{{ source.content }}
**Previous Interactions:**
{{ tools.memory.root }}
Please provide helpful, friendly support based on the knowledge base above.2. Technical Documentation Assistant
You are a technical documentation expert.
**Available Documentation ({{ source.count }} documents):**
{{ source.content }}
**Requirements:**
- Provide code examples in {{ passthrough.language }}
- Focus on {{ passthrough.framework }} best practices
- Include relevant links when possible3. Internal Knowledge Base
You are an internal AI assistant for {{ passthrough.department }}.
**Employee:** {{ passthrough.employee_name }}
**Access Level:** {{ passthrough.access_level }}
**Relevant Documents:**
{{ source.content }}
Provide detailed answers appropriate for {{ passthrough.access_level }} access level.Template Syntax Reference
Variables
{{ variable_name }} # Output variable
{{ namespace.field }} # Access nested field
{{ variable | default("N/A") }} # Default valueConditionals
{% if condition %}
Content
{% elif other_condition %}
Other content
{% else %}
Default content
{% endif %}Loops
{% for item in list %}
{{ item.field }}
{% endfor %}Comments
{# This is a comment and won't appear in output #}Security Considerations
- Input Sanitization: Passthrough data is automatically sanitized to prevent injection attacks
- Type Filtering: Only primitive types (string, int, float, bool, None) are allowed in passthrough
- Autoescaping: Jinja2 autoescaping is enabled by default
- Size Limits: Consider the token budget when including large documents
Troubleshooting
Problem: Variables Not Rendering
Solution: Ensure you’re using the correct namespace:
❌ {{ company }}
✅ {{ passthrough.company }}Problem: Empty Output for Tool Data
Solution: Check that tool pre-fetching is enabled and the tool is configured correctly.
Problem: Syntax Errors
Solution: Validate template syntax. Common issues:
❌ {{ variable } # Missing closing brace
❌ {% if x % # Missing closing %}
✅ {{ variable }}
✅ {% if x %}...{% endif %}Problem: Legacy Prompts Not Working
Solution: The system auto-detects template syntax. If your prompt uses {summaries}, it will work in legacy mode. To use new features, add {{ }} syntax.
API Reference
Render Prompt via API
from application.api.answer.services.prompt_renderer import PromptRenderer
renderer = PromptRenderer()
rendered = renderer.render_prompt(
prompt_content="Your template with {{ passthrough.name }}",
user_id="user_123",
request_id="req_456",
passthrough_data={"name": "Alice"},
docs_together="Document content here",
tools_data={"memory": {"root": "Files: notes.txt"}}
)Conclusion
The new template-based prompt system provides powerful flexibility while maintaining backward compatibility. By leveraging namespaces, you can create dynamic, context-aware prompts that adapt to your specific use case.
Key Benefits:
- ✅ Dynamic variable injection
- ✅ Organized namespaces
- ✅ Backward compatible
- ✅ Security built-in
- ✅ Easy to debug
Start with simple templates and gradually add complexity as needed. Happy prompting! 🚀